Monitor Bandwidth Usage with vnStat

Productivity Sauce
In these days of bandwidth caps and pay-per-kilobyte rates, keeping an eye on your bandwidth usage makes a lot of sense. While there is no lack of bandwidth monitoring utilities, vnStat stands out from the crowd thanks to its ability to store monitoring data in a database and resume monitoring automatically on reboot. This means that once installed and configured, vnStat quietly monitors a specified network interface and saves the collected data. You can then use vnStat's command parameters to view detailed reports of your bandwidth usage.
vnStat is available in the software repositories of many mainstream Linux distributions, so you can easily install it using your distro's package manager. On an Ubuntu-based system, vnStat can be installed using the sudo apt-get install vnstat command. Before you can start using the utility, you must specify the network interface you want vnStat to monitor. First, run the ifconfig command to view a list of all available network interfaces. You can then use the -u and -i parameters to create a database for the specified network interface, for example:
sudo vnstat -u -i wlan0
Once vnstat is configured, it needs some time to collect data. After that you can view the bandwidth usage statistics using the vnstat command. The utility sports a few rather useful parameters, too. The -d ( or --days) parameter displays the daily bandwidth usage, while the -w ( --weeks) and -m ( --months) parameters break down the statistics by week and month. You can view a full list of available parameters using either the vnstat --help or vnstat --longhelp command.
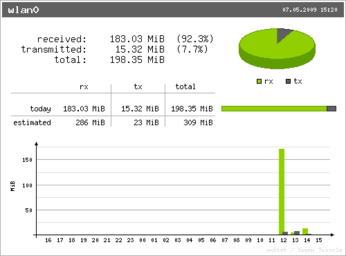
The packaged version of vnStat that is available in your distro's software repositories may not include vnStati -- a nifty utility which can turn dry text-only statistics into nice-looking graphs. In this case, if you want to analyze monitoring data visually, you have to compile vnStat from source. Fortunately, this is a rather straightforward procedure. First of all, make sure that you have all the tools necessary for building software from source. On Ubuntu, you can install them using the sudo apt-get install build-essential command. Next, install the libgd2-noxpm and libgd2-noxpm-dev libraries, using the sudo apt-get install libgd2-noxpm libgd2-noxpm-dev command. Download the latest .tar.gz version of vnStat from the project's Web site and unpack it. Switch to the resulting directory in the terminal and execute the make all command. Finally, run the sudo make install command to install the software. To generate a graph in the PNG format using VnStati, you have to specify at least three parameters: a graph type, a network interface, and the output file. For example, the command below produces a vnstat.png graphics file containing a traffic summary including hourly data using a horizontal layout:
vnstati -vs -i wlan0 -o ~/vnstat.png
Of course, you can use the vstati --help command to view a list of the available parameters.
Comments
comments powered by DisqusSubscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
Kernel 7.0 Now in Testing
Linus Torvalds has announced the first Release Candidate (RC) for the 7.x kernel is available for those who want to test it.
-
Introducing matrixOS, an Immutable Gentoo-Based Linux Distro
It was only a matter of time before a developer decided one of the most challenging Linux distributions needed to be immutable.
-
Chaos Comes to KDE in KaOS
KaOS devs are making a major change to the distribution, and it all comes down to one system.
-
New Linux Botnet Discovered
The SSHStalker botnet uses IRC C2 to control systems via legacy Linux kernel exploits.
-
The Next Linux Kernel Turns 7.0
Linus Torvalds has announced that after Linux kernel 6.19, we'll finally reach the 7.0 iteration stage.
-
Linux From Scratch Drops SysVinit Support
LFS will no longer support SysVinit.
-
LibreOffice 26.2 Now Available
With new features, improvements, and bug fixes, LibreOffice 26.2 delivers a modern, polished office suite without compromise.
-
Linux Kernel Project Releases Project Continuity Document
What happens to Linux when there's no Linus? It's a question many of us have asked over the years, and it seems it's also on the minds of the Linux kernel project.
-
Mecha Systems Introduces Linux Handheld
Mecha Systems has revealed its Mecha Comet, a new handheld computer powered by – you guessed it – Linux.
-
MX Linux 25.1 Features Dual Init System ISO
The latest release of MX Linux caters to lovers of two different init systems and even offers instructions on how to transition.

Additional Tools
If anyone has additional network monitoring needs, let me suggest this website: http://www.activitymonitori...network_server_monitoring1.php
great tip
was easy to install through ubuntu's apt
I am trying to configure vnstat php fontend (http://www.sqweek.com/sqweek/index.php?p=1) must have for a server