Calculating Probability
Features
The Monty Hall problem is loved by statisticians around the world [1]. You might be familiar with this puzzle, in which a game show host offers a contestant a choice of three doors – behind one door is a prize, but the other two doors only reveal goats. After the contestant chooses a door, the TV host opens a different door, revealing a goat, and asks the candidate to reconsider (Figure 1). Who would have thought that probabilities in a static television studio could change so dramatically just because the host opens a door without a prize?
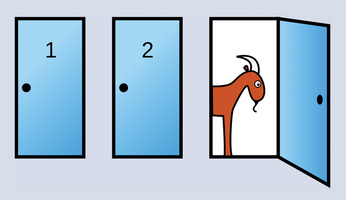 Figure 1: Hoping to win the car, the contestant chooses door 1. The host, who knows which door leads to the car, then opens door 3, revealing a goat. He offers the contestant the option of picking another door. Does it make sense for the contestant to change their mind and go for door 2? (Source: Wikipedia)
Figure 1: Hoping to win the car, the contestant chooses door 1. The host, who knows which door leads to the car, then opens door 3, revealing a goat. He offers the contestant the option of picking another door. Does it make sense for the contestant to change their mind and go for door 2? (Source: Wikipedia)
[...]
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
Buy Linux Magazine
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
Wayland 1.24 Released with Fixes and New Features
Wayland continues to move forward, while X11 slowly vanishes into the shadows, and the latest release includes plenty of improvements.
-
Bugs Found in sudo
Two critical flaws allow users to gain access to root privileges.
-
Fedora Continues 32-Bit Support
In a move that should come as a relief to some portions of the Linux community, Fedora will continue supporting 32-bit architecture.
-
Linux Kernel 6.17 Drops bcachefs
After a clash over some late fixes and disagreements between bcachefs's lead developer and Linus Torvalds, bachefs is out.
-
ONLYOFFICE v9 Embraces AI
Like nearly all office suites on the market (except LibreOffice), ONLYOFFICE has decided to go the AI route.
-
Two Local Privilege Escalation Flaws Discovered in Linux
Qualys researchers have discovered two local privilege escalation vulnerabilities that allow hackers to gain root privileges on major Linux distributions.
-
New TUXEDO InfinityBook Pro Powered by AMD Ryzen AI 300
The TUXEDO InfinityBook Pro 14 Gen10 offers serious power that is ready for your business, development, or entertainment needs.
-
LibreOffice Tested as Possible Office 365 Alternative
Another major organization has decided to test the possibility of migrating from Microsoft's Office 365 to LibreOffice.
-
Linux Mint 20 Reaches EOL
With Linux Mint 20 at its end of life, the time has arrived to upgrade to Linux Mint 22.
-
TuxCare Announces Support for AlmaLinux 9.2
Thanks to TuxCare, AlmaLinux 9.2 (and soon version 9.6) now enjoys years of ongoing patching and compliance.

