ESAPI 1.4: Security Methods for the Web
The Enterprise Security API (ESAPI), a set of documentation focusing on application software security, has released a new version 1.4. Javadocs were updated and old interfaces were replaced.
ESAPI is a product of the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP). The organization collects expertise on securing web applications, holds conferences and develops tools such as the WebScarab HTTP/S analysis proxy. OWASP members range from small consulting firms and security providers like Symantec to industry giants like IBM and Microsoft.
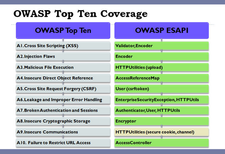
ESAPI describes methods that a typical web app needs for security. These methods include fixing authentication and protecting against cross-site scripting (XSS), cross-site request forgery (XSRF) and SQL injection. Other methods address failure to restrict URL access, insecure communications and improper error handling. The project publishes a Top 10 list of the most serious web app vulnerabilities.
The ESAPI project recommends that developers shouldn't continue to reinvent the security wheel for each application, but base their efforts on OWASP's expertise gained "over a decade of code review and penetration testing of critical enterprise applications."
The API is virtually independent of operating system and programming language, even though the current reference implementation is written in Java along with its Javadoc. Versions for .NET and PHP are planned.
ESAPI's Java implementation requires Java 1.4.2, but Java 1.6 users can uncomment code to make it work for them. The reference implementation is in binary JAR format for downloading. Developers will then have a forum in the OWASP-ESAPI mailing list.
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
Introducing matrixOS, an Immutable Gentoo-Based Linux Distro
It was only a matter of time before a developer decided one of the most challenging Linux distributions needed to be immutable.
-
Chaos Comes to KDE in KaOS
KaOS devs are making a major change to the distribution, and it all comes down to one system.
-
New Linux Botnet Discovered
The SSHStalker botnet uses IRC C2 to control systems via legacy Linux kernel exploits.
-
The Next Linux Kernel Turns 7.0
Linus Torvalds has announced that after Linux kernel 6.19, we'll finally reach the 7.0 iteration stage.
-
Linux From Scratch Drops SysVinit Support
LFS will no longer support SysVinit.
-
LibreOffice 26.2 Now Available
With new features, improvements, and bug fixes, LibreOffice 26.2 delivers a modern, polished office suite without compromise.
-
Linux Kernel Project Releases Project Continuity Document
What happens to Linux when there's no Linus? It's a question many of us have asked over the years, and it seems it's also on the minds of the Linux kernel project.
-
Mecha Systems Introduces Linux Handheld
Mecha Systems has revealed its Mecha Comet, a new handheld computer powered by – you guessed it – Linux.
-
MX Linux 25.1 Features Dual Init System ISO
The latest release of MX Linux caters to lovers of two different init systems and even offers instructions on how to transition.
-
Photoshop on Linux?
A developer has patched Wine so that it'll run specific versions of Photoshop that depend on Adobe Creative Cloud.