Editing and displaying advanced file attributes
Command Line – Advanced File Attributes

© Photo by Viktor Talashuk on Unsplash
The chattr and lsattr commands offer users a convenient way to modify and display advanced file attributes.
Most users are familiar with the usual file attributes. Desktop file managers often list them as properties: the name, path, size, and the dates that the file was created, last accessed, and last modified (Figure 1). Many, too, are familiar with the separate read, write, and execution permissions for a file's owner, group, and other users. However, over the decades, new filesystems, as well as the needs of version control for developers, have developed additional optional attributes. These additional attributes are edited by chattr [1], the equivalent for chown and chmod for permissions, and can be viewed by lsattr [2]. Both commands are included in the e2fsprogs [3] package and are installed by default in most distributions. While the creation of chattr and lsattr was driven by the needs of developers, many of these additional attributes are practical for everyday use as well.
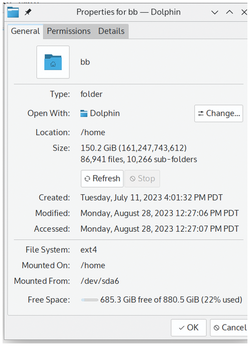 Figure 1: The standard file attributes are displayed in Plasma's Dolphin file manager. Also note the Permissions tab.
Figure 1: The standard file attributes are displayed in Plasma's Dolphin file manager. Also note the Permissions tab.
chattr and lsattr Options
The commands for working with file attributes have limited options. All options use a single letter rather than the full word like GNU style. In chattr, the -f option will suppress all except critical error messages. However, users are more likely to want -R (recursive) to change the attributes of an entire directory or -V (verbose) to receive instant feedback. Developers may want to use -v VERSION together with version control, or -p PROJECT to associate files with a particular project. For commands, chattr uses a standard structure:
[...]
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
Buy Linux Magazine
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
Introducing matrixOS, an Immutable Gentoo-Based Linux Distro
It was only a matter of time before a developer decided one of the most challenging Linux distributions needed to be immutable.
-
Chaos Comes to KDE in KaOS
KaOS devs are making a major change to the distribution, and it all comes down to one system.
-
New Linux Botnet Discovered
The SSHStalker botnet uses IRC C2 to control systems via legacy Linux kernel exploits.
-
The Next Linux Kernel Turns 7.0
Linus Torvalds has announced that after Linux kernel 6.19, we'll finally reach the 7.0 iteration stage.
-
Linux From Scratch Drops SysVinit Support
LFS will no longer support SysVinit.
-
LibreOffice 26.2 Now Available
With new features, improvements, and bug fixes, LibreOffice 26.2 delivers a modern, polished office suite without compromise.
-
Linux Kernel Project Releases Project Continuity Document
What happens to Linux when there's no Linus? It's a question many of us have asked over the years, and it seems it's also on the minds of the Linux kernel project.
-
Mecha Systems Introduces Linux Handheld
Mecha Systems has revealed its Mecha Comet, a new handheld computer powered by – you guessed it – Linux.
-
MX Linux 25.1 Features Dual Init System ISO
The latest release of MX Linux caters to lovers of two different init systems and even offers instructions on how to transition.
-
Photoshop on Linux?
A developer has patched Wine so that it'll run specific versions of Photoshop that depend on Adobe Creative Cloud.
