A home-built virtual RAID with ATA over Ethernet
ATA over Ethernet (AoE) is a protocol for accessing media via Ethernet. A remote client can access the device directly through ATA commands, which the protocol software encapsulates, transmits, and disassembles at the other end (Figure 1). AoE is often used for building low-budget Storage Area Network (SAN) devices. An interesting feature of AoE is that it lets you combine remote disks on different systems into a network-based RAID array. In this article, I describe how to set up AoE and use it to create your own network RAID system.
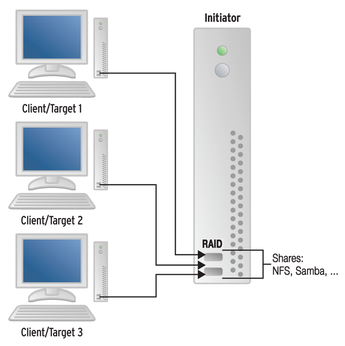 Figure 1: RAID devices over the network with ATA Ethernet follow a pattern similar to iSCSI, with initiators and targets.
Figure 1: RAID devices over the network with ATA Ethernet follow a pattern similar to iSCSI, with initiators and targets.
Required Components
The exact specifications for the AoE protocol are available online [1]: In a style similar to iSCSI, the literature refers to the system that provides the physical disks as a target. The initiator is the system that integrates the disk.
[...]
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
Buy Linux Magazine
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
Parrot OS Switches to KDE Plasma Desktop
Yet another distro is making the move to the KDE Plasma desktop.
-
TUXEDO Announces Gemini 17
TUXEDO Computers has released the fourth generation of its Gemini laptop with plenty of updates.
-
Two New Distros Adopt Enlightenment
MX Moksha and AV Linux 25 join ranks with Bodhi Linux and embrace the Enlightenment desktop.
-
Solus Linux 4.8 Removes Python 2
Solus Linux 4.8 has been released with the latest Linux kernel, updated desktops, and a key removal.
-
Zorin OS 18 Hits over a Million Downloads
If you doubt Linux isn't gaining popularity, you only have to look at Zorin OS's download numbers.
-
TUXEDO Computers Scraps Snapdragon X1E-Based Laptop
Due to issues with a Snapdragon CPU, TUXEDO Computers has cancelled its plans to release a laptop based on this elite hardware.
-
Debian Unleashes Debian Libre Live
Debian Libre Live keeps your machine free of proprietary software.
-
Valve Announces Pending Release of Steam Machine
Shout it to the heavens: Steam Machine, powered by Linux, is set to arrive in 2026.
-
Happy Birthday, ADMIN Magazine!
ADMIN is celebrating its 15th anniversary with issue #90.
-
Another Linux Malware Discovered
Russian hackers use Hyper-V to hide malware within Linux virtual machines.

