Control your Rasp Pi projects with Python’s Tkinter library
The Tinkerer
© Lead Image © agor2012, 123RF.com
Use Tkinter to control your Rasp Pi projects from a smartphone or tablet.
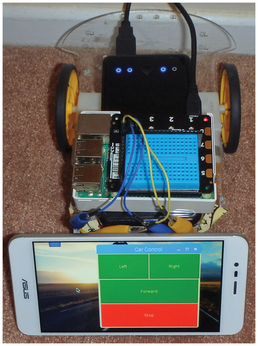
If you are looking for an easy way to control your Raspberry Pi projects, consider Python's Tkinter library. In about 20 lines of Python code, you can create a graphic program to control a Rasp Pi rover project (Figure 1). This article shows how to create a Python Tkinter application to control the Rasp Pi's General Purpose Input Output (GPIO) pins. I will also show you how to set up a desktop shortcut that you can use to easily launch the application, and I will configure a Virtual Network Computing (VNC) server so that a smartphone, tablet, or PC can control the Rasp Pi remotely.
Python Tkinter Library
Tkinter [1] is bundled with the standard Rasp Pi Python installation. The base Tkinter library contains 17 different widgets that you can use for graphic applications. These widgets can be defined with customizable colors, sizes, text, and commands. There are three geometry managers (Pack, Grid, and Place) that can be used to arrange the widgets. For Rasp Pi hardware projects, I found the Grid geometry manager was a good fit. Listing 1 is a simple test program that presents two buttons in a grid and prints feedback when the buttons are pressed. (Note: Python 2.7 references the library as Tkinter, whereas Python 3 uses tkinter, lowercase). Figure 2 shows this test program with some button feedback.
[...]
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
Buy Linux Magazine
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
Introducing matrixOS, an Immutable Gentoo-Based Linux Distro
It was only a matter of time before a developer decided one of the most challenging Linux distributions needed to be immutable.
-
Chaos Comes to KDE in KaOS
KaOS devs are making a major change to the distribution, and it all comes down to one system.
-
New Linux Botnet Discovered
The SSHStalker botnet uses IRC C2 to control systems via legacy Linux kernel exploits.
-
The Next Linux Kernel Turns 7.0
Linus Torvalds has announced that after Linux kernel 6.19, we'll finally reach the 7.0 iteration stage.
-
Linux From Scratch Drops SysVinit Support
LFS will no longer support SysVinit.
-
LibreOffice 26.2 Now Available
With new features, improvements, and bug fixes, LibreOffice 26.2 delivers a modern, polished office suite without compromise.
-
Linux Kernel Project Releases Project Continuity Document
What happens to Linux when there's no Linus? It's a question many of us have asked over the years, and it seems it's also on the minds of the Linux kernel project.
-
Mecha Systems Introduces Linux Handheld
Mecha Systems has revealed its Mecha Comet, a new handheld computer powered by – you guessed it – Linux.
-
MX Linux 25.1 Features Dual Init System ISO
The latest release of MX Linux caters to lovers of two different init systems and even offers instructions on how to transition.
-
Photoshop on Linux?
A developer has patched Wine so that it'll run specific versions of Photoshop that depend on Adobe Creative Cloud.