Deploying Debian systems with FAI
Swirl

© Inge Knittel, Fotolia
FAI helps you automate the process of installing and configuring new Debian systems.
The Fully Automatic Installation (FAI) framework developed at the University of Cologne, Germany, relieves the headache of mass installing Debian systems. FAI offers several customization features and allows you to set up virtual systems. The new 3.2.9 [1] version supports Debian Lenny and includes a new partioning tool.
How It Works
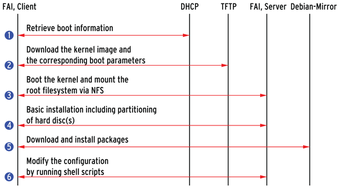
FAI manages the installation process by automating the steps executed by the Debian installer. As shown in Figure 1, an FAI server system runs the FAI daemon and also hosts the services necessary to support network-based installation, including NFS, TFTP, and DHCP. In the most basic scenario, a client with a preboot execution environment (PXE)-based network adapter remote boots, gets an IP address from the DHCP server, then obtains the necessary files through TFTP to launch the remote installation.
[...]
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
Buy Linux Magazine
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
Nitrux 6.0 Now Ready to Rock Your World
The latest iteration of the Debian-based distribution includes all kinds of newness.
-
Linux Foundation Reports that Open Source Delivers Better ROI
In a report that may surprise no one in the Linux community, the Linux Foundation found that businesses are finding a 5X return on investment with open source software.
-
Keep Android Open
Google has announced that, soon, anyone looking to develop Android apps will have to first register centrally with Google.
-
Kernel 7.0 Now in Testing
Linus Torvalds has announced the first Release Candidate (RC) for the 7.x kernel is available for those who want to test it.
-
Introducing matrixOS, an Immutable Gentoo-Based Linux Distro
It was only a matter of time before a developer decided one of the most challenging Linux distributions needed to be immutable.
-
Chaos Comes to KDE in KaOS
KaOS devs are making a major change to the distribution, and it all comes down to one system.
-
New Linux Botnet Discovered
The SSHStalker botnet uses IRC C2 to control systems via legacy Linux kernel exploits.
-
The Next Linux Kernel Turns 7.0
Linus Torvalds has announced that after Linux kernel 6.19, we'll finally reach the 7.0 iteration stage.
-
Linux From Scratch Drops SysVinit Support
LFS will no longer support SysVinit.
-
LibreOffice 26.2 Now Available
With new features, improvements, and bug fixes, LibreOffice 26.2 delivers a modern, polished office suite without compromise.