Map projection on a two-dimensional terminal with Go
Programming Snapshot – Go Map Projections

© Photo by Don Pinnock on Unsplash
While searching for a method to draw geodata right into the terminal, Mike Schilli discovers the wondrous world of map projections.
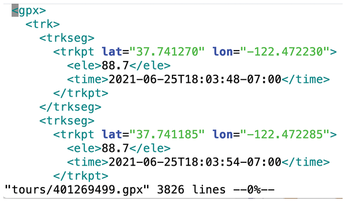
While I was working on hikefind, a command-line program that chooses a trail from a collection of GPX files with track points, for a recent issue [1], I got the idea of drawing the trail contours the program found in a terminal window. Unfortunately, a GPX file generated by an app such as Komoot or a Garmin tracker only contains geocoordinates as floating-point numbers. They refer to the points of the globe through which the trail passes (Figure 1).
These geopoints on a spherical surface now need to be converted to a two-dimensional coordinate system so that they look as natural as possible on a flat map. This problem was solved centuries ago. Any map, whether paper or digital, is based on the genius idea of projecting geopoints on the globe, which are available as latitude and longitude values, onto an XY coordinate system on a plane.
[...]
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
Buy Linux Magazine
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
Linux Foundation Reports that Open Source Delivers Better ROI
In a report that may surprise no one in the Linux community, the Linux Foundation found that businesses are finding a 5X return on investment with open source software.
-
Keep Android Open
Google has announced that, soon, anyone looking to develop Android apps will have to first register centrally with Google.
-
Kernel 7.0 Now in Testing
Linus Torvalds has announced the first Release Candidate (RC) for the 7.x kernel is available for those who want to test it.
-
Introducing matrixOS, an Immutable Gentoo-Based Linux Distro
It was only a matter of time before a developer decided one of the most challenging Linux distributions needed to be immutable.
-
Chaos Comes to KDE in KaOS
KaOS devs are making a major change to the distribution, and it all comes down to one system.
-
New Linux Botnet Discovered
The SSHStalker botnet uses IRC C2 to control systems via legacy Linux kernel exploits.
-
The Next Linux Kernel Turns 7.0
Linus Torvalds has announced that after Linux kernel 6.19, we'll finally reach the 7.0 iteration stage.
-
Linux From Scratch Drops SysVinit Support
LFS will no longer support SysVinit.
-
LibreOffice 26.2 Now Available
With new features, improvements, and bug fixes, LibreOffice 26.2 delivers a modern, polished office suite without compromise.
-
Linux Kernel Project Releases Project Continuity Document
What happens to Linux when there's no Linus? It's a question many of us have asked over the years, and it seems it's also on the minds of the Linux kernel project.