Getting Started with Knoppix 7.3
Go Live!
ByKnoppix 7.3 comprises the current state of Debian GNU/Linux development and comes with the current hardware support of kernel 3.13, a new update function, and extended security and privacy features.
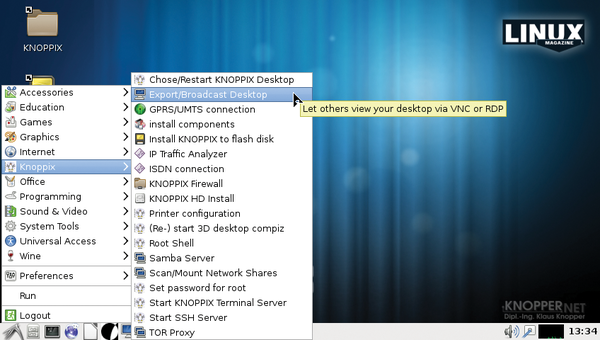
Keeping a distro current with GNU/Linux development can be quite difficult. Debian’s boot system and hardware support via udev can make it difficult for the developer of a Linux distribution to figure out what needs to change just to boot up. Lucky for me, Knoppix’s boot system again proved to be a big timesaver. Knoppix completely works around the Debian default startup systems (Upstart/systemd) by using knoppix-autoconfig, a single shell script that does all the work of preconfiguration (Figures 1 and 2). Kernel support for devtmpfs had to be enabled to get the new udev hardware detection and removable device support working again, but the rest of the transition to the Debian testing branch (pre-jessie) went pretty smoothly.
Knoppix on Flash – Now with Update
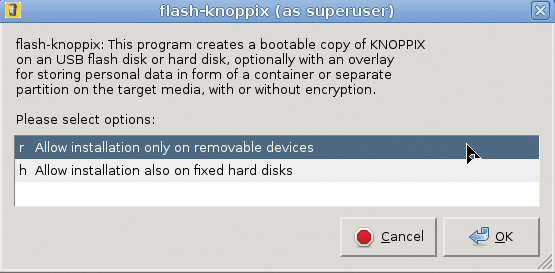
Many modern netbooks and ultrabooks do not even have a DVD drive anymore, so Knoppix is commonly used on a USB flash disk instead of a DVD. Because creating a bootable USB flash disk is probably the first thing you want to do, Knoppix 7.3 now prominently shows an icon for the Knoppix flash disk installation program at the top left of the desktop when booting from DVD (Figures 3 and 4). Even though the Knoppix DVD version is read-optimized by a sort list, which tries to reduce the slow seek speed of the laser read sensor, flash memory boosts startup and the working speed of Knoppix by a factor of at least five. Startup time from loading the kernel to a full desktop with Compiz takes less than 15 seconds if you have recent computer hardware and fast flash pen drives.
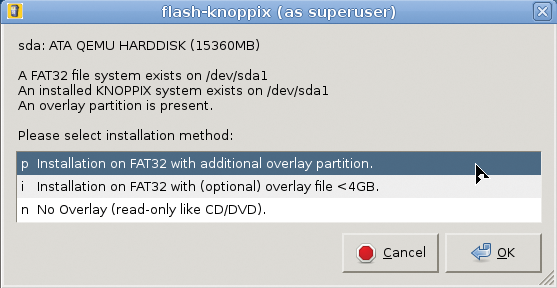
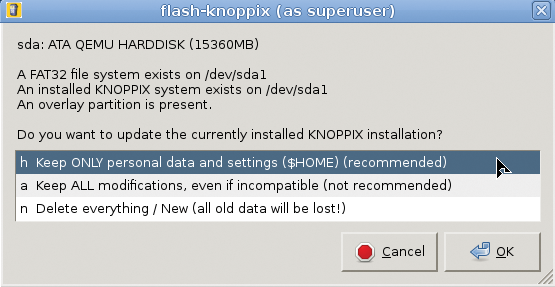
One of the features most asked for last year was the ability to upgrade. Flash-knoppix, the Knoppix flash disk installation program, now scans the target drive for an existing Knoppix installation (Figure 5) and offers to replace just the main compressed filesystem and kernel, instead of installing everything from scratch.
You have an option to keep just personal data (your /home/knoppix directory containing all your files and settings; Figure 6) or additional software outside your home directory (which is not recommended, because software packages installed by the user could be incompatible with the new system).
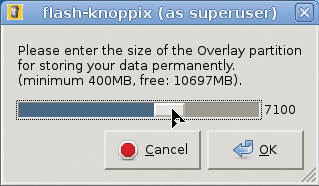
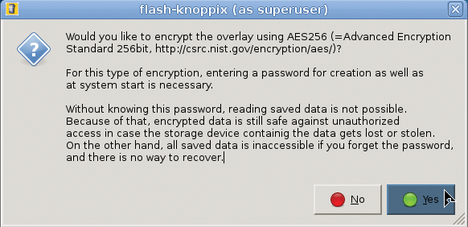
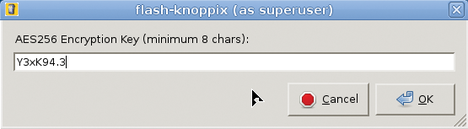
For the update to work, be sure to make enough space available on your flash pen for the full content of the DVD the first time you install. A first partition of 4.5GB should be fine. The Knoppix writable data partition, which is new since Knoppix 7.1, can then spawn over the remaining capacity of the flash drive (Figure 7) with optional encryption (Figures 8 and 9) that protects your passwords and personal files if you ever lose your flash drive or it gets stolen.
EFI and Hybrid CD/Flash Boot
Booting from flash is quick and easy because all changes and stored files are written to the data partition automatically. Some computers still can’t boot from flash drives, though, either because they are too old (i.e., the BIOS does not have an option for booting from USB) or because they have boot firmware like EFI that does not allow booting from external hard disks.
An efi directory on the first partition of the Knoppix-installed drive contains all the files needed to boot on an EFI-aware computer. If the EFI firmware is set to “Secure Boot,” booting from anything but the “allowed” operating system is impossible. If in doubt, choose the “CSM” boot option in your computer’s BIOS. CSM in EFI is the official abbreviation for “Compatibility Support Module,” but it means “boot normally” (with the traditional boot record and bootloader from disk).
If your computer still can’t boot from a USB drive, Knoppix 7.3 includes a very small (12MB) CD-ROM ISO image in the KNOPPIX directory that you can burn to an empty CD-R. In this way, you can start your computer when both the boot-only CD and the USB flash drive are attached. After first starting from the boot-only CD, the system automatically switches to the USB drive and continues booting from there. This workaround is known to work well even on Macs, which have restrictive USB boot capabilities.
Security and Privacy
Security and privacy have always been at the top of Knoppix architectural design, even before last year’s increased awareness of security resulting from various surveillance revelations. The popular Firefox browser – named Iceweasel in Debian – comes with the NoScript plugin in sharp mode. With only a few preset exceptions, NoScript asks for attention and permission whenever your browser loads a web page with “active content” that would trigger plugins or execute potentially dangerous scripts, including JavaScript.
A yellow message on the bottom status bar tells you when content has been blocked. You can disable checks for a website you trust during a browser session only or permanently (e.g., if you want to watch flash movies that require plugin activity and access to the computer hardware). NoScript makes online banking and Internet transactions a lot safer, because it also catches cross-site scripting attacks and warns even in the case of “suspicious” content.
Many users asked about a firewall in Knoppix. In other operating systems, a firewall is necessary because they have open ports reachable from the Internet. Knoppix, however, is preconfigured with no services running on the external network interfaces by default (unless you explicitly start Samba or VNC, the remote desktop server). A port scanner thrown at a Knoppix system with no firewall running will not find any attackable open port.
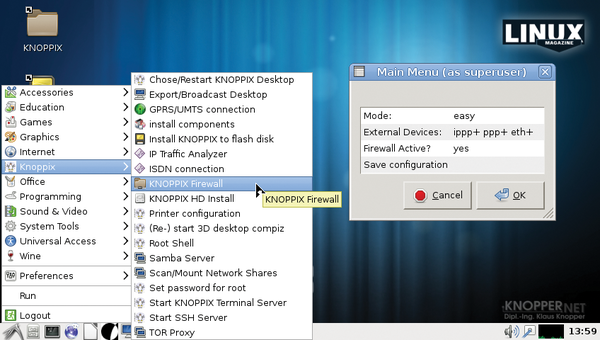
However, Knoppix does have an easy-to-use firewall setup script (Figure 10) that allows you to add filters that let services either run locally only or be accessible from the local network only. The firewall comes with three levels of complexity, from easy to expert (which lets you add your own iptables rules). Again, starting a firewall is not required for normal use of Knoppix as a secure client to access the Internet. In the case of video conferences, for example, a firewall can even be counterproductive, depending on the software used.
All accounts are blocked on Knoppix, with no “backdoor” password – not even for the default, unprivileged knoppix user. Therefore, a “login” is impossible. If you manage to start a screen locker, you are effectively locked out. (For this reason, I disabled the automatic lock screen features of various desktop managers.) The only ways to “break in” to a Knoppix system is to be logged in already, to start the secure shell server (SSH) and set a password, or to start the VNC server so remote access is possible (Figure 11). By the way, the knoppix user is allowed to execute programs as root using sudo for recovery tasks.
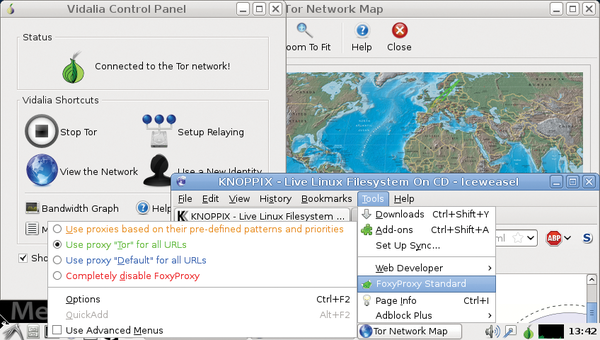
Privacy is the main goal of the Tor network (Tor = The onion router) by making it difficult for malicious or advertising websites to detect your location and identity. Using a complex mesh of participating routers on the Internet, Tor effectively suppresses the ability to trace your physical address. Websites only see the address of the so-called “exit node,” which is a random computer enabled as a router inside the Tor network. Tor can be enabled by a starter application in the Knoppix menu and has to be set up as a “proxy” in the web browser of your choice.
A single-click option for Tor has already been added to Firefox and Chromium, so enabling Tor is quite easy (Figure 12). However, please be aware that Tor is not designed to be used for secure transactions and authenticated services. If you need to access an authenticated service, such as online banking, I recommend turning off the Tor proxy for this purpose.
Knoppix PXE Boot Server
You can set up Knoppix as a boot server for the local network, so that other computers, acting as clients, can boot from the server, access the Knoppix medium remotely, and run programs locally. For this task, Start KNOPPIX Terminal Server in the Knoppix menu. Setup is easy and straightforward; you basically just confirm the allowed network range and boot options for the clients. In this way, you can run an entire classroom with just one physical Knoppix medium. In version 7.3, I have changed the terminal server setup to generally provide 32-bit clients (64-bit computers still boot in 32-bit compatibility mode, of course), even if the host system was booted with the knoppix64 boot option. This setup is the most compatible for clients, and does not require clients to specify the kernel with which to boot.
Boot Problems?
Normally, Knoppix does not require any boot options to determine the correct settings for your hardware, graphics cards, and so on. However, with so many different chipsets and combinations thereof, it is sometimes necessary to disable a feature or hardware component temporarily to reach the productive desktop stage.
Some common boot options for hardware problems are listed in the boot help that you can reach by hitting F2 or F3 in the boot screen; others are listed in the text file knoppix-cheatcodes.txt inside the KNOPPIX directory. If the desktop gets stuck at the point that the 3D composite window manager Compiz should start, try booting with
knoppix nocomposite
or
knoppix no3d
to disable the graphics subsystem’s “composite” extension, or just to avoid starting Compiz.
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
Parrot OS Switches to KDE Plasma Desktop
Yet another distro is making the move to the KDE Plasma desktop.
-
TUXEDO Announces Gemini 17
TUXEDO Computers has released the fourth generation of its Gemini laptop with plenty of updates.
-
Two New Distros Adopt Enlightenment
MX Moksha and AV Linux 25 join ranks with Bodhi Linux and embrace the Enlightenment desktop.
-
Solus Linux 4.8 Removes Python 2
Solus Linux 4.8 has been released with the latest Linux kernel, updated desktops, and a key removal.
-
Zorin OS 18 Hits over a Million Downloads
If you doubt Linux isn't gaining popularity, you only have to look at Zorin OS's download numbers.
-
TUXEDO Computers Scraps Snapdragon X1E-Based Laptop
Due to issues with a Snapdragon CPU, TUXEDO Computers has cancelled its plans to release a laptop based on this elite hardware.
-
Debian Unleashes Debian Libre Live
Debian Libre Live keeps your machine free of proprietary software.
-
Valve Announces Pending Release of Steam Machine
Shout it to the heavens: Steam Machine, powered by Linux, is set to arrive in 2026.
-
Happy Birthday, ADMIN Magazine!
ADMIN is celebrating its 15th anniversary with issue #90.
-
Another Linux Malware Discovered
Russian hackers use Hyper-V to hide malware within Linux virtual machines.