Tips for mixing safely
Mixology

© Lead Image © Andrey-Kiselev, 123RF.com
A little caution can save you hours of frustrating work (plus, options for mixing gone awry).
Debian package repositories are organized along two axes. The first axis controls the degree of software freedom in the installation. Newly installed, a Debian system includes only packages from the main section of the repository, which contains only free-licensed packages. However, you can enable the contrib section, which houses free packages that depend on non-free packages, and non-free, which houses packages with restrictive licenses, by editing the URLs for repositories in /etc/apt/sources.list (Figure 1). Little harm can come from this editing, and, in fact, it is necessary if you want to use the advanced proprietary hardware drivers. The second axis, though, is another matter. Tinkered with carelessly, it causes more reinstalls than any other aspect of Debian.
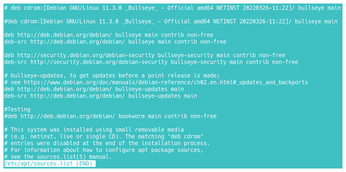 Figure 1: The sources.list file contains the addresses of all repositories used by a Debian system. Note that the cdrom used to install is disabled by commenting out, and that all three sections of repositories are listed. Only the stable and testing repositories are listed.
Figure 1: The sources.list file contains the addresses of all repositories used by a Debian system. Note that the cdrom used to install is disabled by commenting out, and that all three sections of repositories are listed. Only the stable and testing repositories are listed.
This second axis is the main Debian repositories themselves. By default, a Debian system enables only the stable repository. Stay with stable and you enjoy the full support of the distribution, including backports and security updates. But set up the testing and unstable repositories intended primarily for developers, and nothing is guaranteed. A single careless step, and you could lose your desktop environment, the ability to work with packages, or some other basic part of the installation, and find yourself condemned to hours of futile efforts to recover. Too often, a reinstall [1] is the quickest solution.
[...]
Buy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)
Buy Linux Magazine
Subscribe to our Linux Newsletters
Find Linux and Open Source Jobs
Subscribe to our ADMIN Newsletters
Support Our Work
Linux Magazine content is made possible with support from readers like you. Please consider contributing when you’ve found an article to be beneficial.

News
-
Introducing matrixOS, an Immutable Gentoo-Based Linux Distro
It was only a matter of time before a developer decided one of the most challenging Linux distributions needed to be immutable.
-
Chaos Comes to KDE in KaOS
KaOS devs are making a major change to the distribution, and it all comes down to one system.
-
New Linux Botnet Discovered
The SSHStalker botnet uses IRC C2 to control systems via legacy Linux kernel exploits.
-
The Next Linux Kernel Turns 7.0
Linus Torvalds has announced that after Linux kernel 6.19, we'll finally reach the 7.0 iteration stage.
-
Linux From Scratch Drops SysVinit Support
LFS will no longer support SysVinit.
-
LibreOffice 26.2 Now Available
With new features, improvements, and bug fixes, LibreOffice 26.2 delivers a modern, polished office suite without compromise.
-
Linux Kernel Project Releases Project Continuity Document
What happens to Linux when there's no Linus? It's a question many of us have asked over the years, and it seems it's also on the minds of the Linux kernel project.
-
Mecha Systems Introduces Linux Handheld
Mecha Systems has revealed its Mecha Comet, a new handheld computer powered by – you guessed it – Linux.
-
MX Linux 25.1 Features Dual Init System ISO
The latest release of MX Linux caters to lovers of two different init systems and even offers instructions on how to transition.
-
Photoshop on Linux?
A developer has patched Wine so that it'll run specific versions of Photoshop that depend on Adobe Creative Cloud.
